Q 1/20
0
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
lift is greater than the gross weight.
B
lift equals weight plus the vertical component of the drag.
C
thrust equals drag plus the uphill component of the gross weight in the flight path direction.
D
thrust equals drag plus the downhill component of the gross weight in the flight path direction.
Explanation
Thrust = Drag + WSineTheta
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
Total Lift
B
Vertical Lift
C
Non-essential Lift
D
Horizontal lift
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
Drag exceeds thrust
B
Life = Weight
C
Lift is greater than weight
D
Lift is less than weight
Explanation
In order to overcome weight , the lift force has to be greater in order for the aircraft to climb
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
41%
B
10%
C
19%
D
45%
Explanation
sqrt(1/cos(45))
Explanation Provided by Max Davy
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
A faster speed will result in a smaller radius of turn
B
A faster speed will result in no change of radius to our turn
C
Slower speed will result in a larger radius of turn
D
A faster speed will result in a larger radius of turn
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
Just above the stall speed, or as slow as possible
B
The speed giving the maximum drag
C
The critical angle of attack where lift is the highest
D
The speed giving the minimum drag of the aircraft
Explanation
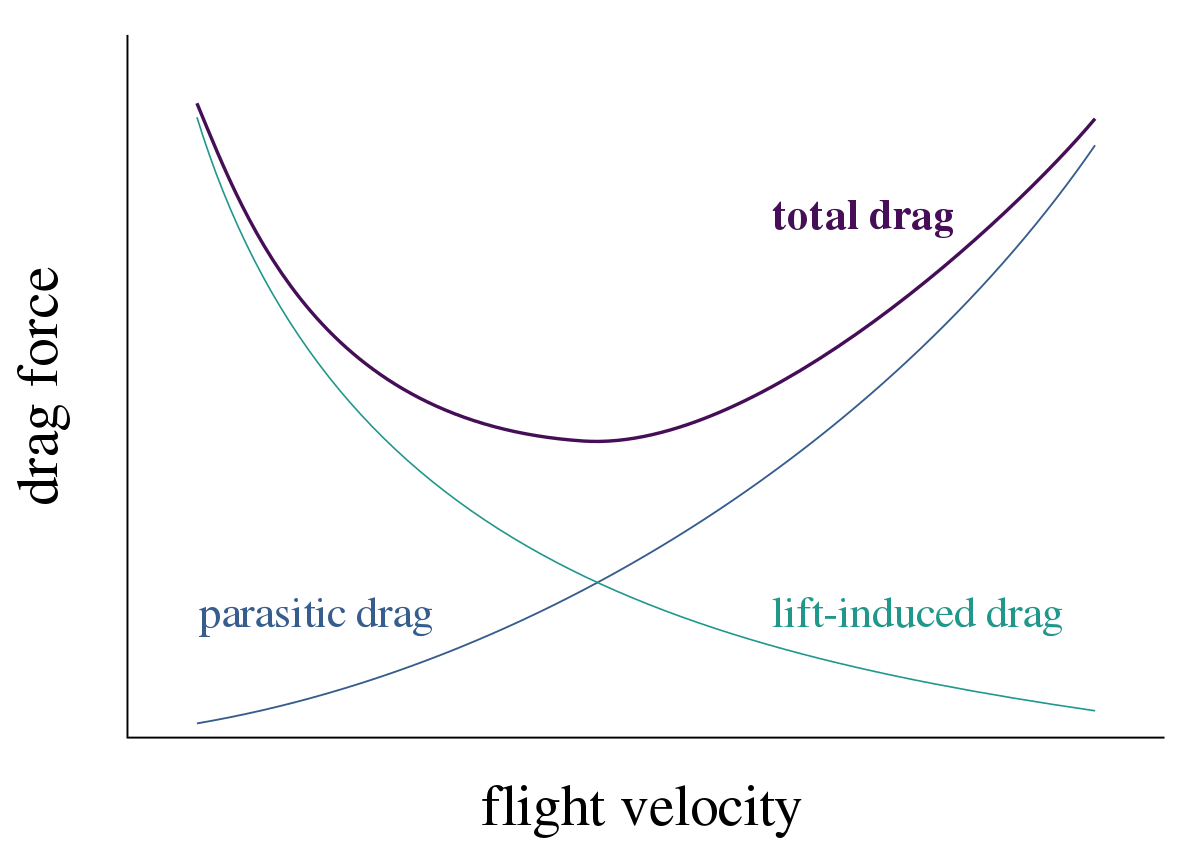
The speed where minimum drag is found is the best glide speed, it can be our instinct to fly the aircraft at the lowest speed possible thinking it will extend our glide but it won`t as the the stall speed is not where drag is the least, nor is flying at the speed that gives us maximum lift, we have to find the balance and this is known as our VMD(outside the scope) but this is maximum lift to drag ratio of the aircraft , its an important number to know for your aircraft as it may save your life! always fly the aircraft at this speed in an engine failure, not faster, not slower, but right on the numbers till you know you can safely make the runway
See attached image for the drag curve
See attached image for the drag curve
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
A headwind.
B
A tailwind.
C
A decrease in mass.
D
An increase in mass.
Explanation
Decreasing mass will allow you to glide for a longer time, but you will glide no further in distance
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
may increase or decrease depending on the type of aeroplane.
B
increases
C
remains the same.
D
decreases.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
Gradient of climb for a given power setting will be higher.
B
Flight endurance will be increased.
C
Stalling speeds will be lower.
D
Stalling speeds will be higher.
Explanation
Stall speed increases with an increase in mass.
New Vs = Old Vs x √New weight ÷ Old weight
New Vs = Old Vs x √New weight ÷ Old weight
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
Decrease & Decrease
B
Increase & Increase
C
Decrease & Increase
D
Increase & Decrease
Explanation
If we look the basic formula Gradient = (Thrust - Drag) / Weight
which means if we increase the denominator (i.e: the weight) and keep the excess thrust constant (i.e: the resultant of Thrust minus Drag) this will provide a lower climb gradient. Conversely if we reduce the weight the climb gradient will become steeper. One can conclude that an increase in aircraft mass will reduce the max climb gradient and therefore increase the Vx and Vy since the nose of the aircraft will be lower and more able to gain speed faster, thus; giving the aforementioned increase in Vx and Vy.
which means if we increase the denominator (i.e: the weight) and keep the excess thrust constant (i.e: the resultant of Thrust minus Drag) this will provide a lower climb gradient. Conversely if we reduce the weight the climb gradient will become steeper. One can conclude that an increase in aircraft mass will reduce the max climb gradient and therefore increase the Vx and Vy since the nose of the aircraft will be lower and more able to gain speed faster, thus; giving the aforementioned increase in Vx and Vy.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
A tailwind will decrease the flight path angle and decrease the descent angle.
B
A tailwind will decrease the flight path angle and the descent angle will remain constant.
C
A tailwind will increase the flight path angle and decrease the descent angle.
D
In a tailwind, the flight path angle will remain constant and the descent angle will remain constant.
Explanation
The flight path angle is basically the angle between the speed vector (i.e: where the aircraft is going, not where the nose is pointing) and the horizontal. In a tailwind this angle reduces.
Descent angle is NEVER affected by wind. The descent angle will be the same however the point where the airplane will hit the ground will be different, in tailwind will be further away whereas; in a headwind will be closer, but the angle with which the descent will be made is exactly the same.
Descent angle is NEVER affected by wind. The descent angle will be the same however the point where the airplane will hit the ground will be different, in tailwind will be further away whereas; in a headwind will be closer, but the angle with which the descent will be made is exactly the same.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
the speed for best angle of flight path.
B
the speed for best angle of climb.
C
the speed for best rate of climb.
D
the speed for best specific range.
Explanation
VX = Speed for Best Angle of Climb. It allows us to have the maximum climb angle to clear obstacles which are close in to the aerodrome departure area like a mountain or other obstacle. VX is a slow speed and will allow a sharper angle.
Explanation Provided by Saqib Raja
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
VY
B
VCL
C
VX
D
V2
Explanation
An aircraft climbs as a result of excess thrust or excess power. Vx is the best angle of climb speed, and Vy is the best rate of climb speed.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
Yaw left
B
Climb
C
Roll right
D
Sink
Explanation
Removing the flaps will cause the aircraft to initially sink as you remove that "extra" bit of lift you was initially allowing the flaps to generate and need to compensate by increasing the pitch of the aircraft
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
flaps
B
fuselage-mounted speed brakes.
C
slats
D
spoilers
Explanation
By re-energising the airflow going over the top of the wing
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
spring balance
B
Stronger cables
C
Mass balance
D
Anti-balance tab
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
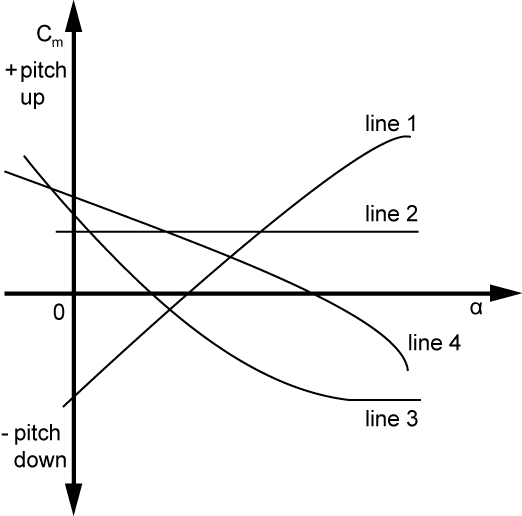
A
Line 4.
B
Line 3.
C
Line 2.
D
Line 1.
Explanation
This is the Cm/alpha graph. The more stable a plane is, the steeper the line will be going downwards from left to right will be. Line 4 starts at the top left and goes downwards towards bottom right. It steepens towards the end. This shows stability at all AoA. Many mistake line 3, but at the end it shows neutral stability as the line evens off.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
The induced angle of attack and induced drag decrease.
B
The thrust required will increase significantly.
C
The wing tip vortices increase in strength.
D
The wing downwash on the tail surfaces increases.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
at the origin.
B
below the origin.
C
to the left of the origin.
D
above the origin.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %
This question has been flagged as being in an exam by multiple students, give it more attention
A
below the origin.
B
at the origin.
C
above the origin.
D
to the right of the origin.
Your Right answers are 0 out of and Your Percentage is: 0 %